Oil and gas separators installed in 100,000 kilometers of the crown
The relationship between engine oil and carbon deposition
This is a problem faced by all automobile engines at present. When the oil enters the cylinder to participate in the combustion of gasoline, the piston will accumulate more carbon, and the engine will burn oil ahead of schedule. Why do some cars start burning oil at 100000 kilometers? while others burn oil for 500000 kilometers, the nature is completely different, so car owners pay more and more attention to the problem of engine carbon deposition. From so many brands of carbon deposition cleaners in the automotive aftermarket, modified breathable kettle, walnut sand and dry ice inlet technology to “dig coal”, all of them are products developed because of the problem of carbon deposition in the engine cylinder, then what is engine carbon deposition? Why does the engine accumulate carbon? What is the most important reason for carbon accumulation in automobile engines?
Brief introduction of forced ventilation of engine crankcase
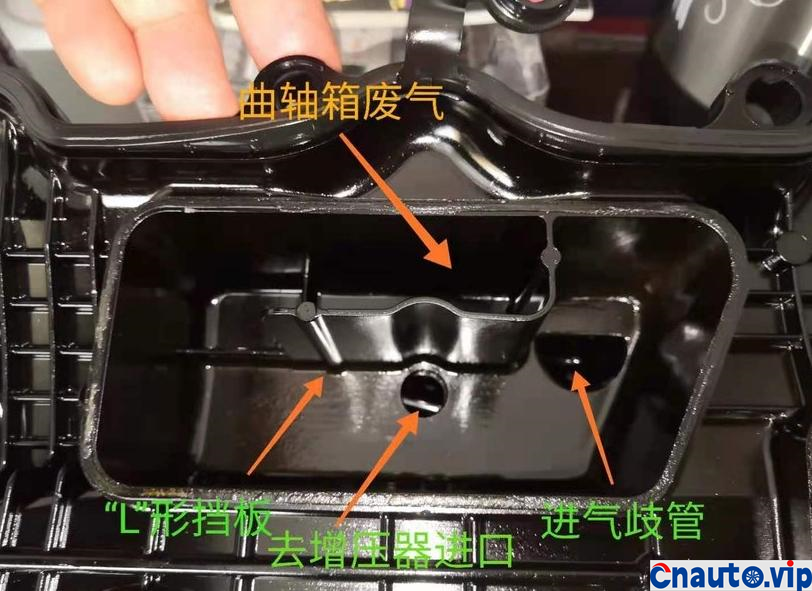
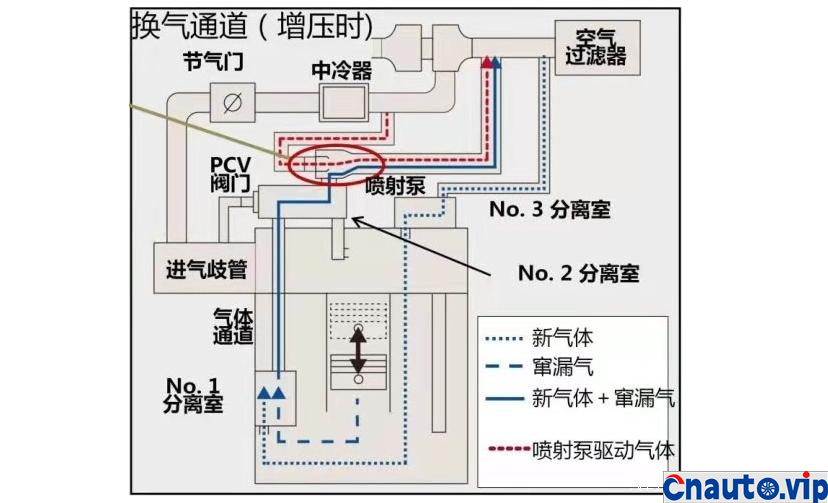
During the operation of the engine, a small part of the high pressure gas produced by the engine will rush into the crankcase through the opening of the piston ring, which is called exhaust gas. A small amount of combustible gas and water vapor in the composition will pollute the oil in the crankcase and lead to a decline in the lubrication performance of the oil. In addition, due to the requirements of environmental protection, the waste gas from the crankcase is not allowed to be discharged directly into the atmosphere and pollute the environment. Therefore, automobile engines are designed with crankcase forced ventilation system, through the pressure difference before and after the throttle, fresh air into the crankcase to bring exhaust gas to the cylinder for secondary combustion, and then discharged through the ternary catalytic converter!
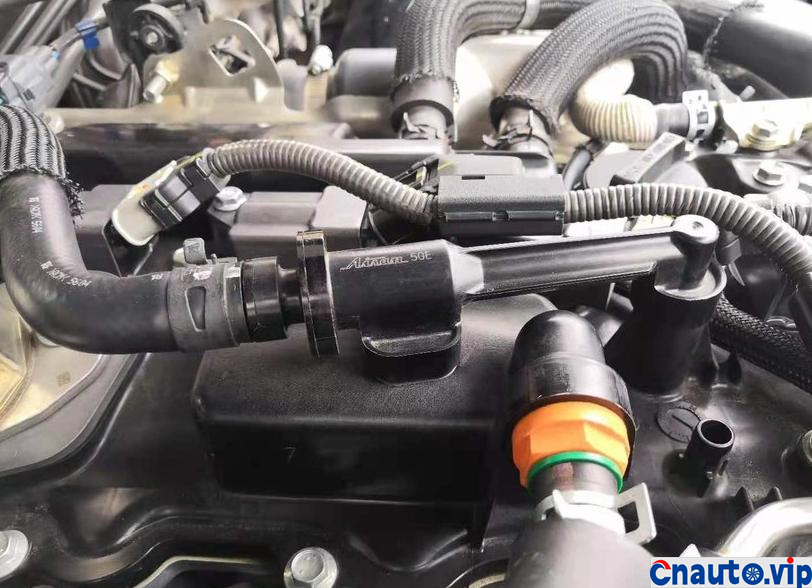
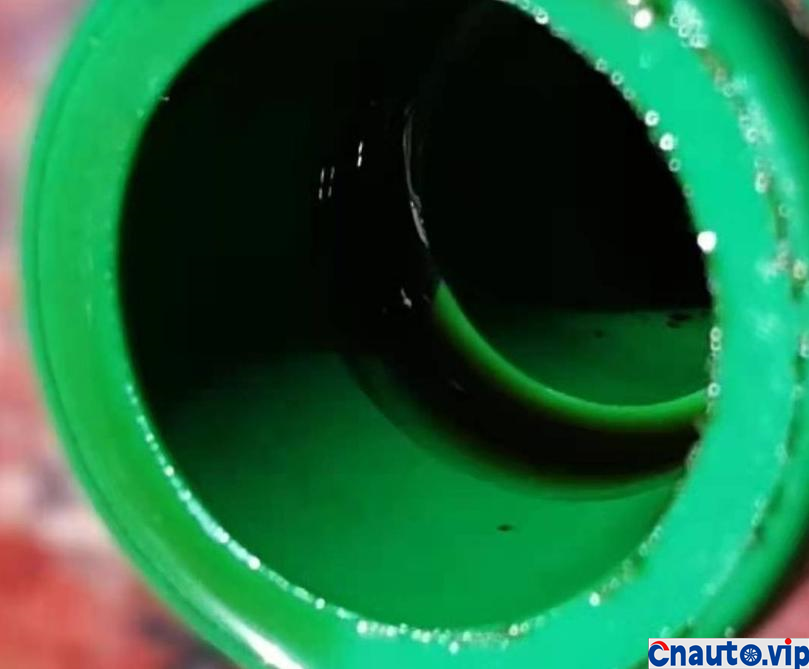
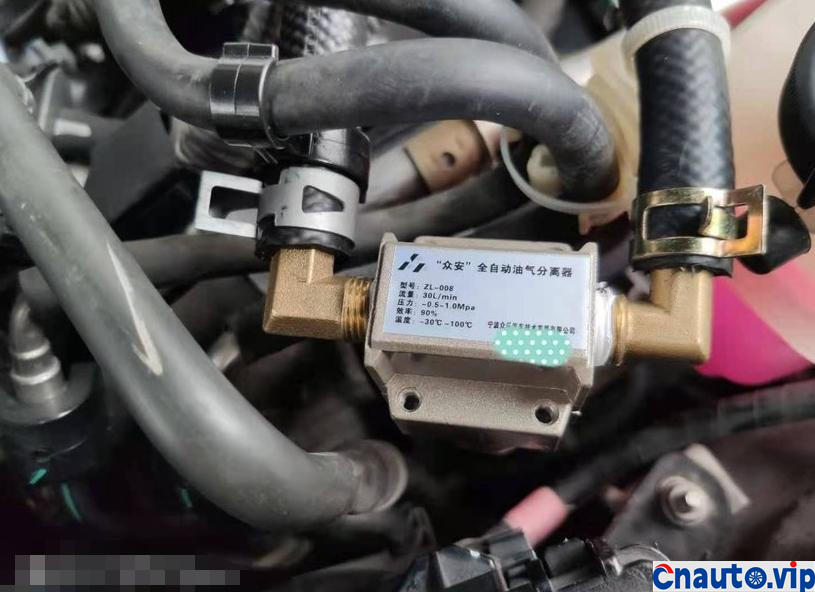
The piston and cylinder liner of the engine are lubricated by the oil thrown out of the connecting rod when the crankshaft rotates, and the interior of the engine crankcase is filled with foggy oil, which will be brought into the intake system with forced ventilation. although the crankcase forced ventilation system of automobile engine has oil and gas separation device, most of them are maze and baffle principle, and the effect of oil and gas separation is very general.
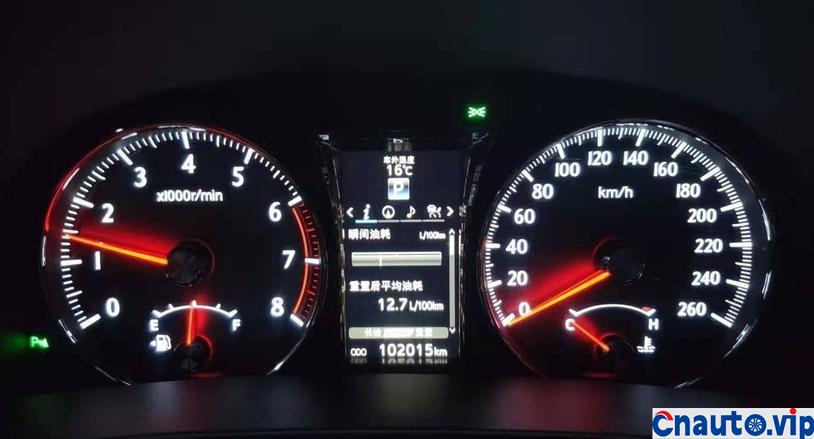
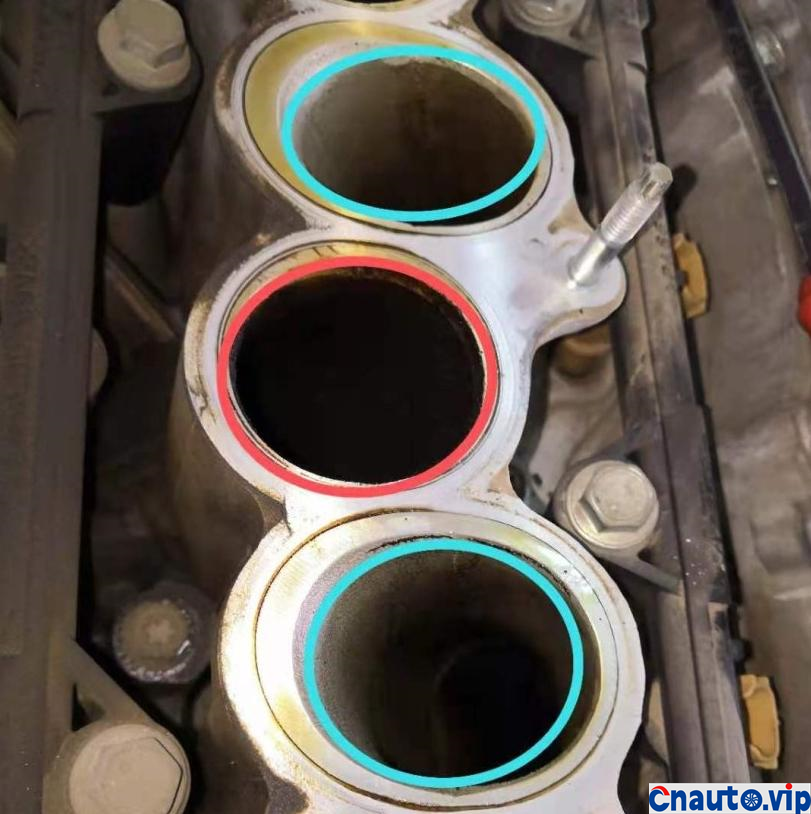
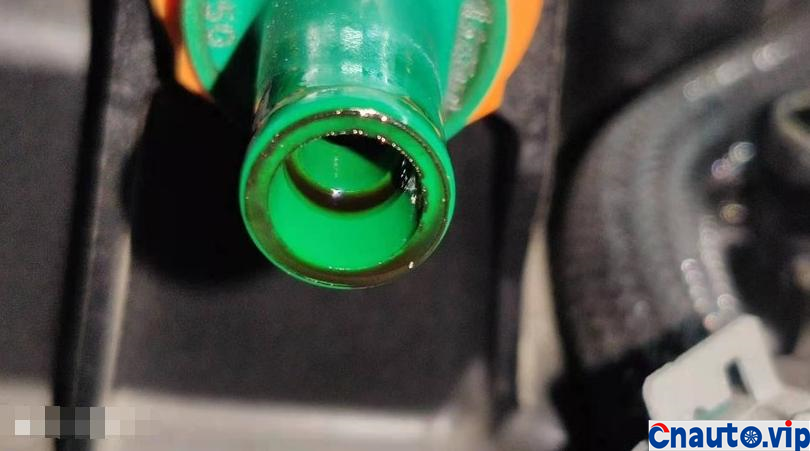
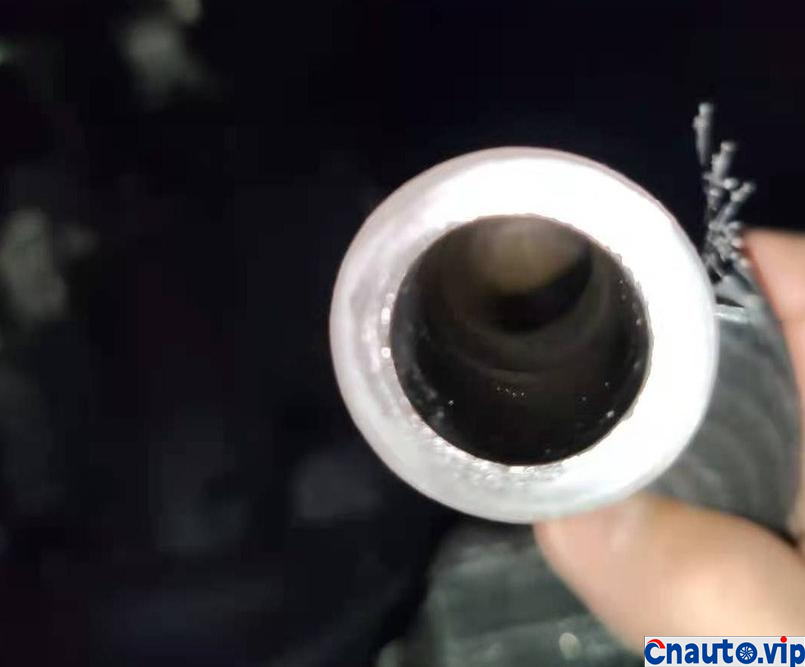
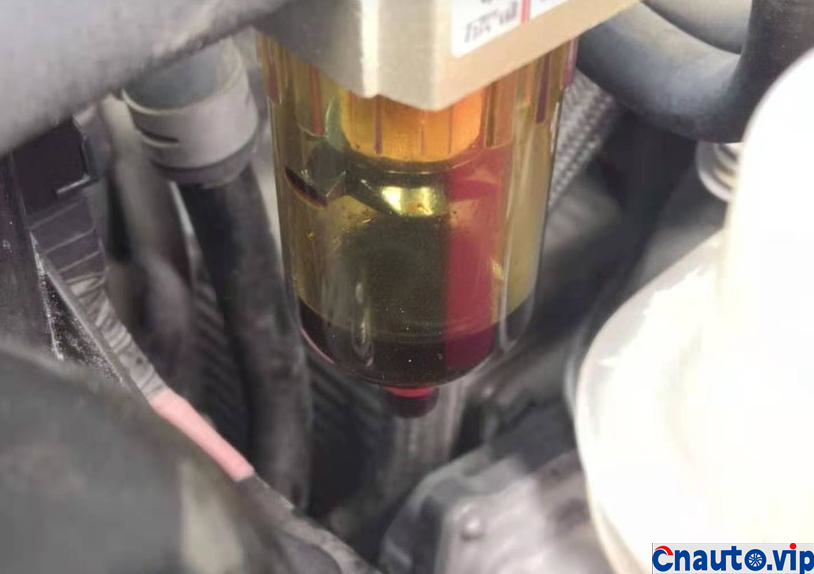
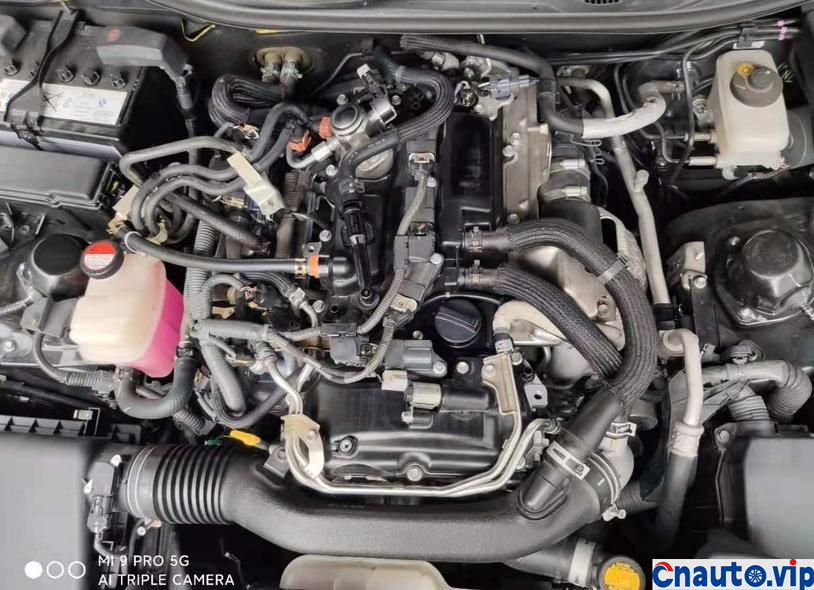
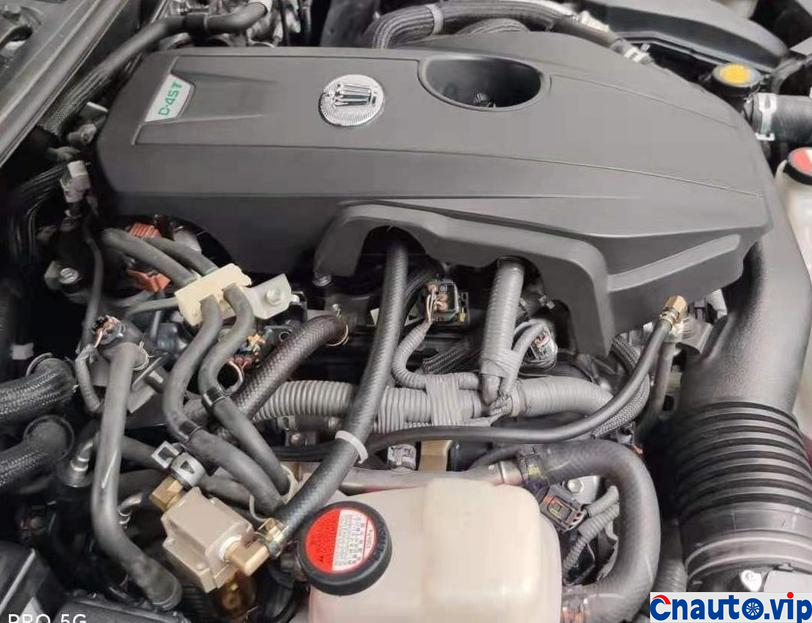
Toyota Crown’s 2.0T turbocharged engine, model 8AR-FTS, is also used in models such as the Halanda and Lexus. It claims that it does not burn oil. Its own car has a mileage of 100000 kilometers, and the oil consumption of the engine is stable at 10000km / 0.2L (200mL). It should be the best oil control among the turbocharged engines at present. However, 50,0.1 litres (100mL) of engine oil is burned through the intake pipe suction cylinder into sludge and carbon deposits!
Excelsior, to reduce carbon deposition should be actively prevented, not passive cleaning
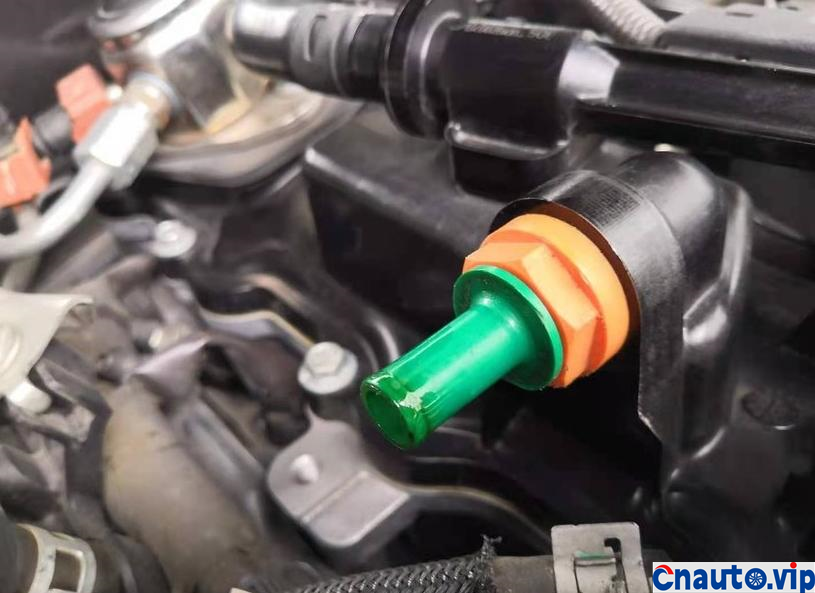
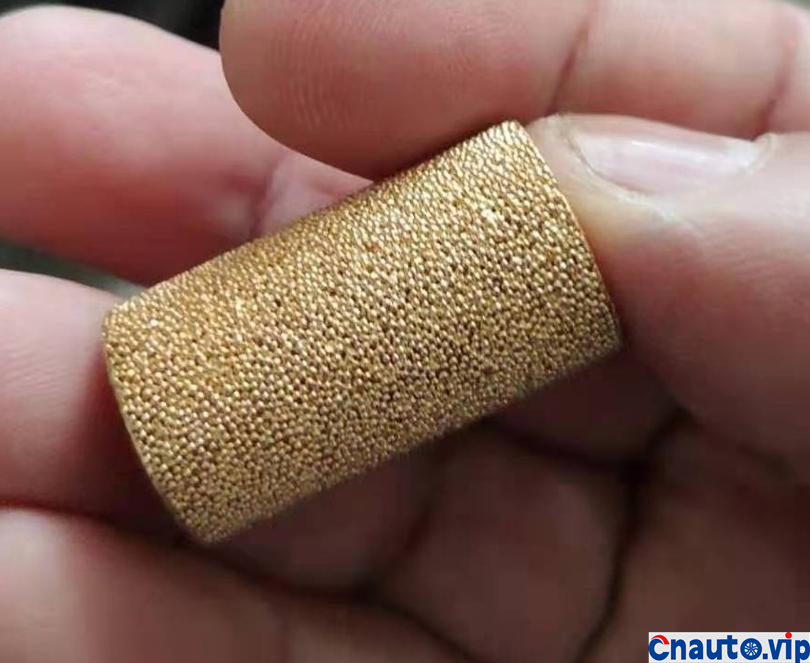
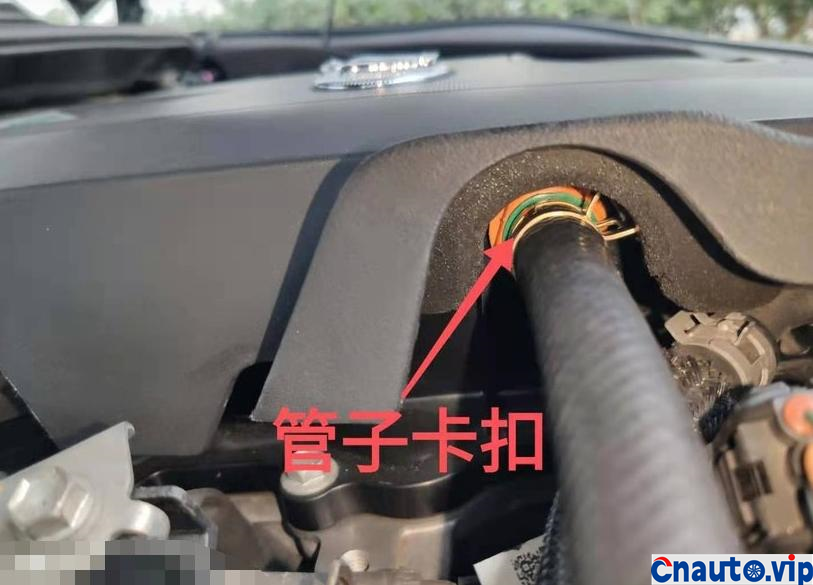
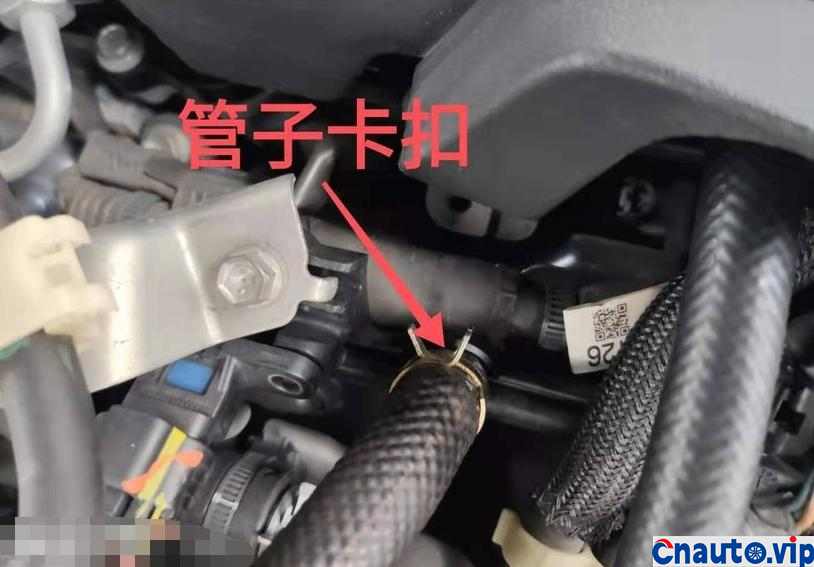
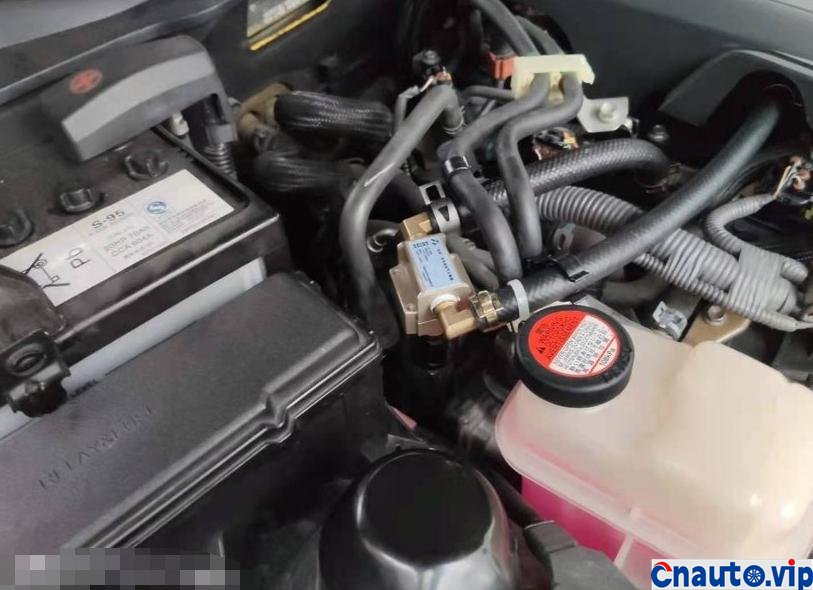
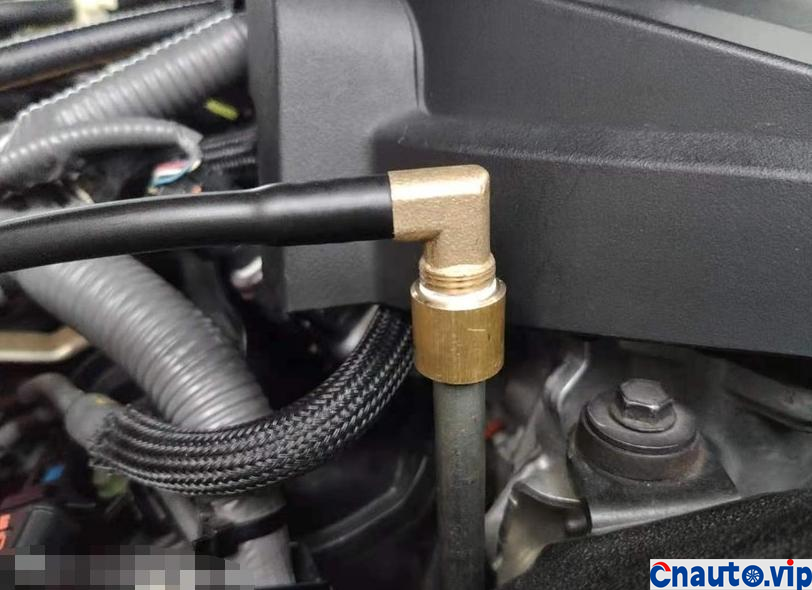
The engine oil consumption of the original car decreased by 4mm every 10000 km, the oil ruler was scaled up and down to 36mm/1.7L, the oil was 0.2L, and there was no change at 90000 km. Through the 10000 km test through the separator, the oil consumption was reduced by half, that is to say, the original oil consumption: intake pipe abnormal consumption 0.1L + piston ring, valve oil seal and other normal lubrication consumption 0.1L. The modified oil-steam separator is specially designed for the turbocharged engine, which finely separates the waste gas containing more oil in the intake manifold of the original factory, so that the oil separation rate is more than 90%, and the oil is automatically recovered to the oil pan of the engine, which not only reduces the sludge and carbon accumulation in the cylinder of the intake system, but also reduces the oil consumption!




















 April 1, 2024
April 1, 2024  March 27, 2024
March 27, 2024 
 March 27, 2024
March 27, 2024